Explain to Me the Difference Between Charge and Current
Electric current is defined as a stream of charged particlessuch as electrons or ionsmoving through an electrical conductor or space. Current is calculated by dividing voltage by the resistance.

Electrical Energy Power And Charge
Voltage is measured in volts V Current is measured in amps A Resistance is measured in ohms Ω Power is measured in watts W Electrical power or the wattage of an electrical system is always equal to the voltage multiplied by the current.

. The current is known as the flow of charge or electrons. Unsplash What is AC power. Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive.
The electrons are free to move from one atom to another. It is the steady state of a constant-voltage circuit. Current is the rate at which charge is flowing.
16 10 19 C The flow of electrons is termed electron current. The difference between AC and DC mainly includes the following. Electrons are negatively charged and are therefore attracted to the positive terminal as unlike charges attract.
You always measure voltage as a voltage difference between two points. Most well-known applications however use a time-varying voltage source. The SI unit for current is ampere which is named in honor of Andre-Marie Ampere.
Electric charge in alternating current AC on the other hand changes direction periodically. In this equation V stands for voltage and I stands for current. Both AC and DC describe types of current flow in a circuit.
In metals the charge carrier is the electron whose charge is negative by definition note negative sign. The other differences between the static and current electricity are explained below in the comparison. The consistent and constant voltage of DC.
Electric charge in alternating current AC on the other hand changes direction periodically. Overview of Electric Charge Ampere Electric Field of a Point Charge Current Electricity Static Electrcity. Electron Flow The electron flow is from negative to positive terminal.
The conventional current flow is from positive to the negative terminal and indicates the direction that positive charges would flow. Current is measured in Amperes or A. Voltage also called electromotive force is the potential difference in charge between two points in an electrical field.
Electric current is expressed mathematically eg. In your home it is eaten by corded appliances small and large from your HVAC to your TV and dishwasher. Most of the digital electronics that you build will use DC.
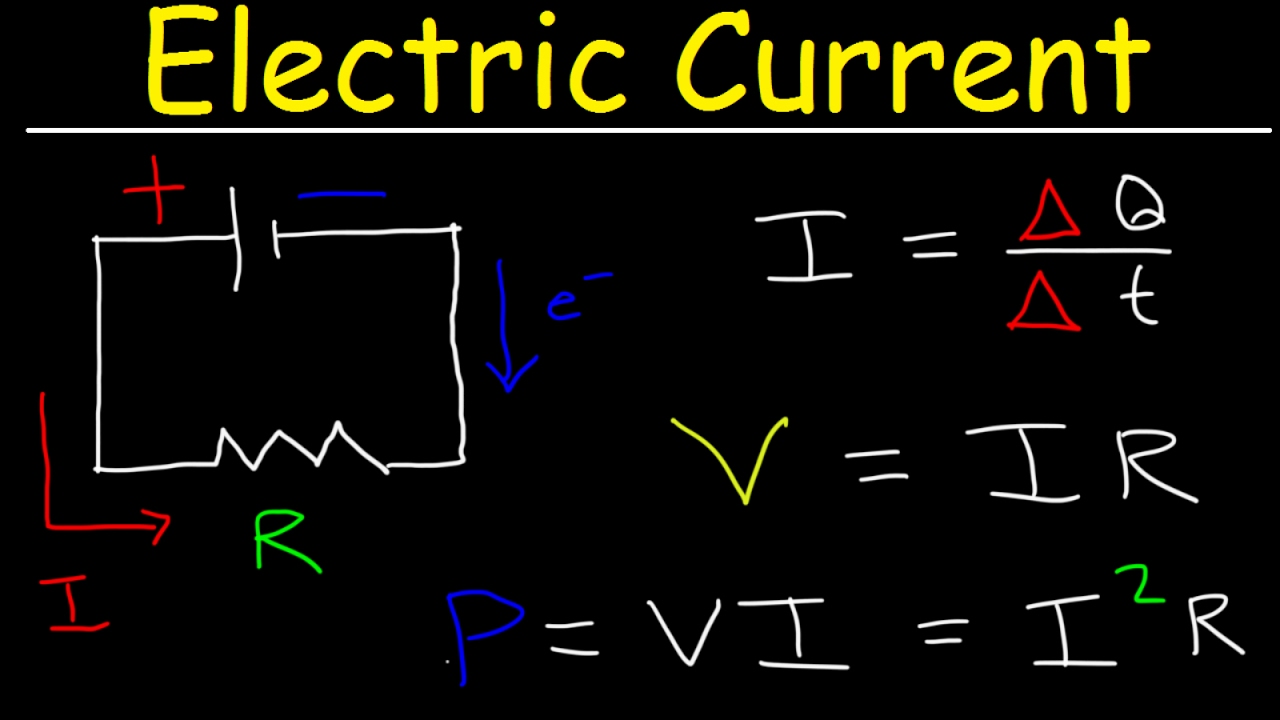
Charge Q is measured in coulombs C current I is measured in amperes A time t is measured in seconds s One ampere is the current that flows when one coulomb of charge passes a point in a. The clog itself would be the resistance. Fun Safe Electricity Experiments for Kids.
Voltage is calculated as the difference between two points while current is defined as the rate at which a given charge is flowing. These charges are usually in the form of electrons. Direct current DC is the flow of electric charge in only one direction.
Alternating current AC is the flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction. So when we talk about these values were really describing the movement of. In direct current DC the electric charge current only flows in one direction.
In other words voltage is the energy per unit charge. In direct current the charges flow by keeping the constant magnetism along the wire. Current is defined as the rate of flow of charges through a medium.
Difference between AC and DC Alternating Current AC Alternating current is defined as the flow of charge that changes direction periodically. Then also the current indicates directions in a direction from positive to the negative end. In other words current is the rate of flow of electric charge.
Voltage is the difference in charge between two points. Resistance is a materials tendency to resist the flow of charge current. A or amps or amperage.
This electrical energy is transferred in the circuit into light heat and movement. Voltage measures the energy carried by the charge flowing in a circuit. The electrons flow from the negative end of the battery to the positive end of the battery.
It is the flow rate of electric charge through a conducting medium with respect to time. Resistance is measured in Ohms or Ω. Conventionalcurrentor simply current behaves as if positive charge carriers cause current.
The voltage in AC circuits also periodically reverses because the current changes direction. A system of water pipes is often used as an analogy to help people understand how these units of. The charges in the alternating current flow either by rotating a coil in the magnetic field or by rotating a magnetic field within a stationary coil.
Properties of Electric Current. The symbol for current is I it is measured in amperes A. Your home or office receives electricity in the form of wave-like AC current which is capable of changing direction and voltage from higher to lower current with the aid of transformers.
The direction of the current depends on the direction of the flow of charge. This difference in pressure between the two points is the equivalent to voltage. Charge current times time The symbol for charge is Q it is measured in coulombs C.
Current is a flow of electrical charge. We call them a sea of delocalised electrons. Voltage is measured in Volts or V.
One coulomb is the quantity of charge transferred in one second Mathematically the definition of a coloumb is represented as. In formulas using the symbol I or i. In direct current DC the electric charge current only flows in one direction.
The result obtained will be the. Current is the rate at which electric charge flows past a point in a circuit. Current was originally defined as the flow of.
The electric current can be identified as the current that is caused by the flow of charges in the direction of the charges flow. The most significant difference between the static and current electricity is that in static electricity the charges are at rest and they are accumulating on the surface of the insulator. Q It In the equation Q is the electric charge I is the electric current and t is the time.
We now know this is incorrect. Whereas in current electricity the electrons are moving inside the conductor.

Electric Current Definition Unit Formula Properties Types Electricity Current Current Electric

Electric Current About Me Blog Electric Flux Current Electric
Electric Current Circuits Explained Ohm S Law Charge Power Physics Problems Basic Electricity Youtube

Comments
Post a Comment